Introduction (Tariffs)
In recent years, international trade has been at the forefront of economic discussions, particularly with the United States implementing various tariff measures under President Donald Trump’s administration. These actions have significantly influenced global markets, notably affecting India’s economy and its trade dynamics with the U.S. This report aims to elucidate the concepts of tariffs, import duties, and reciprocal tariffs, delve into their historical context, and analyze their implications on India-U.S. trade relations.
What Are Tariffs ?
A tariff is a tax imposed by a government on imported goods and services. The primary objectives of tariffs are to:
- Protect Domestic Industries: By making imported goods more expensive, tariffs encourage consumers to buy domestically produced products.
- Generate Revenue: Tariffs serve as a source of income for governments.
- Regulate Trade: They can be used as tools to negotiate trade terms or retaliate against unfair trade practices.
It’s essential to distinguish between tariffs and duties. While both are forms of taxes on imports, duties are specific charges imposed on particular goods, often based on the item’s value, weight, or quantity. In contrast, tariffs are broader taxes applied to categories of imports from specific countries.
Historical Context of U.S. Tariffs
The United States has a long history of utilizing tariffs as economic tools:
- 19th Century: Tariffs were a significant source of federal revenue, with rates among the highest globally between 1861 and 1933.
- Post-World War II: The U.S. shifted towards promoting free trade, leading to the reduction of tariff barriers and the establishment of international trade agreements.
- Recent Developments: Under President Trump’s administration, there was a resurgence of protectionist policies, with tariffs imposed on various countries to address trade imbalances and protect domestic industries.
Understanding Reciprocal Tariffs
Reciprocal tariffs refer to the practice of a country imposing tariffs equivalent to those levied by its trading partners. The rationale is to ensure fair trade by matching the trade barriers that other countries impose. However, this approach has its challenges:
- Complexity: Determining equivalent tariffs can be intricate due to differences in economic structures and product valuations.
- Potential for Trade Wars: Reciprocal tariffs can escalate tensions, leading to retaliatory measures and broader trade conflicts.
India-U.S. Trade Dynamics
The trade relationship between India and the United States has seen significant shifts over the years. According to a CNN Business article published on February 11, 2025, the trade deficit between the U.S. and India has been widening, with the United States importing $45.7 billion more from India than it exported.
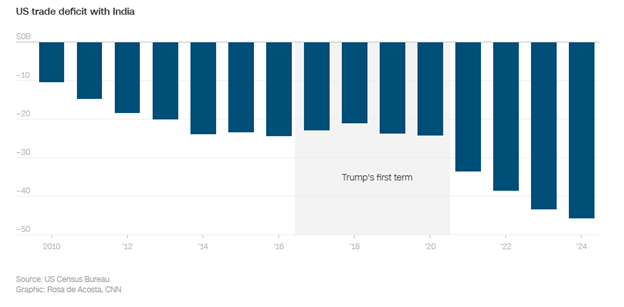
This growing trade imbalance has been a point of contention, leading to increased scrutiny and the imposition of tariffs.
The Big Picture: Why India-US Trade Matters
India and the U.S. have a strong and growing trade relationship, with total bilateral trade crossing $130 billion in 2023. The U.S. is India’s largest trading partner, and India is a key market for American goods and services.
- India exports mainly pharmaceuticals, gems, textiles, and IT services to the U.S.
- India imports crude oil, aircraft, machinery, and medical equipment from the U.S.
What comes in and what goes out
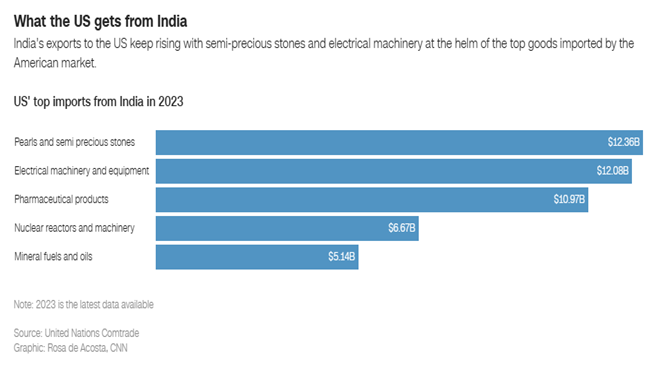
The chart shows the top goods that the U.S. imported from India in 2023. Pearls and semi-precious stones were the biggest category at $12.36 billion, followed closely by electrical machinery and equipment at $12.08 billion. Pharmaceutical products, which include medicines, were also a major export, worth $10.97 billion. Other key imports were nuclear reactors and machinery ($6.67 billion) and mineral fuels and oils ($5.14 billion). This data highlights India’s strong position in supplying gems, technology, and pharmaceuticals to the U.S. market.
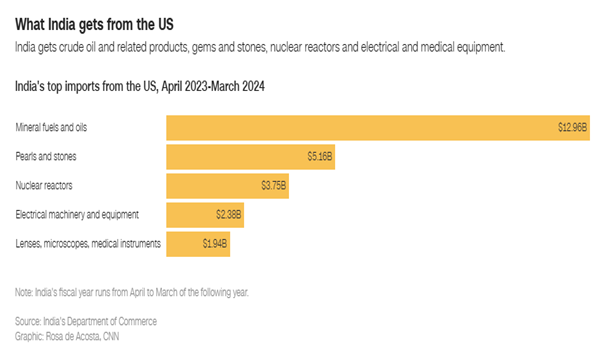
The chart shows India’s top imports from the U.S. between April 2023 and March 2024. Mineral fuels and oils were the largest import, valued at $12.96 billion, highlighting India’s dependence on U.S. energy resources. Pearls and stones followed at $5.16 billion, showing demand for high-value gems. Other key imports included nuclear reactors ($3.75 billion), electrical machinery and equipment ($2.38 billion), and medical instruments ($1.94 billion).
Impact of U.S. Tariffs on India
India has been significantly affected by the U.S.’s tariff measures:
- Export Challenges: The U.S. is a major market for Indian goods. Increased tariffs have made Indian products less competitive, potentially reducing export volumes.
- Economic Implications: Sectors like textiles, pharmaceuticals, and automotive components have faced increased costs, impacting profitability and employment.
- Policy Responses: To mitigate these effects, India has considered reducing tariff on over 50% of U.S. imports worth $23 billion, aiming to negotiate relief from U.S. tariff.
Effects on Indian Equity and Commodity Markets
The imposition of tariffs has reverberated through India’s financial markets:
- Market Volatility: Uncertainty surrounding trade policies has led to fluctuations in stock prices, especially for companies reliant on exports.
- Commodity Price Shifts: Tariff on commodities have altered demand-supply dynamics, affecting prices and impacting producers and consumers alike.
- Investor Sentiment: The apprehension of escalating trade wars has made investors cautious, influencing investment decisions and capital flows.
Recommendations for Traders and Investors
Given the current trade environment, stakeholders should consider the following strategies:
- Diversification: Spread investments across sectors and geographies to mitigate risks associated with specific tariff.
- Stay Informed: Regularly monitor trade policy developments to anticipate market movements and adjust strategies accordingly.
- Focus on Domestic Markets: Investing in companies with a strong domestic presence can reduce exposure to international trade uncertainties.
- Hedging: Utilize financial instruments to hedge against potential losses stemming from trade-related market volatility.
Conclusion
Tariffs are pivotal tools in international trade, influencing economic relations and market dynamics. The recent tariff measures by the U.S. have posed challenges for India, impacting its exports and economic sectors. Understanding the nuances of tariff, their historical context, and current implications is crucial for traders, investors, and policymakers to navigate this complex landscape effectively.
Until then, Happy Trading!
Commodity Samachar Securities
We Decode the Language of the Markets
Also Read: Trump Auto Tariffs Loom—Which Ones Will Hit First? , Bulls vs Bears – The Ultimate Showdown This Monthly Expiry! Who Will Dominate?
Recommended Read: India’s Semiconductor Surge: Powering the Future of Electronics!
Want Help On Your Trades ?
Chat with RM